View a live demo at dockerfile.onmiget.com.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:- A Miget account at app.miget.com
- Git installed on your local machine
- A Dockerfile in your application repository
- Basic familiarity with Docker and command line operations
Prepare Your Application
Clone the sample Docker application to your local machine:Create and Deploy Your App
Create a new app
Navigate to app.miget.com and click the New button, then select Application.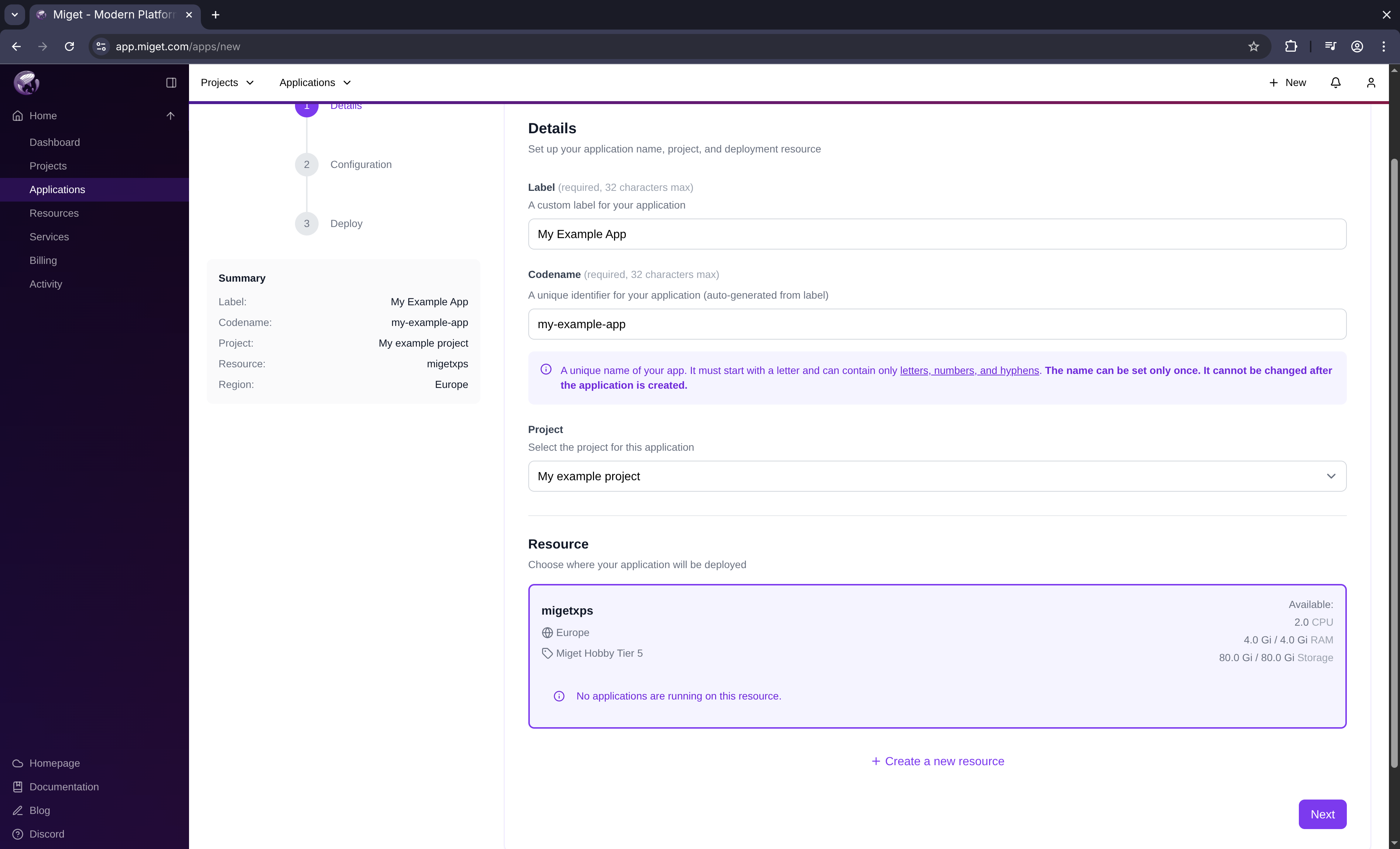 In the Create new App window:
In the Create new App window:

- Enter your App Name
- Select the resource where you want to deploy
- Click Next
Miget automatically appends a unique suffix to your app name (e.g.,
example-1jgiq) to ensure uniqueness.Configure builder and size
Configure your app’s build and runtime settings: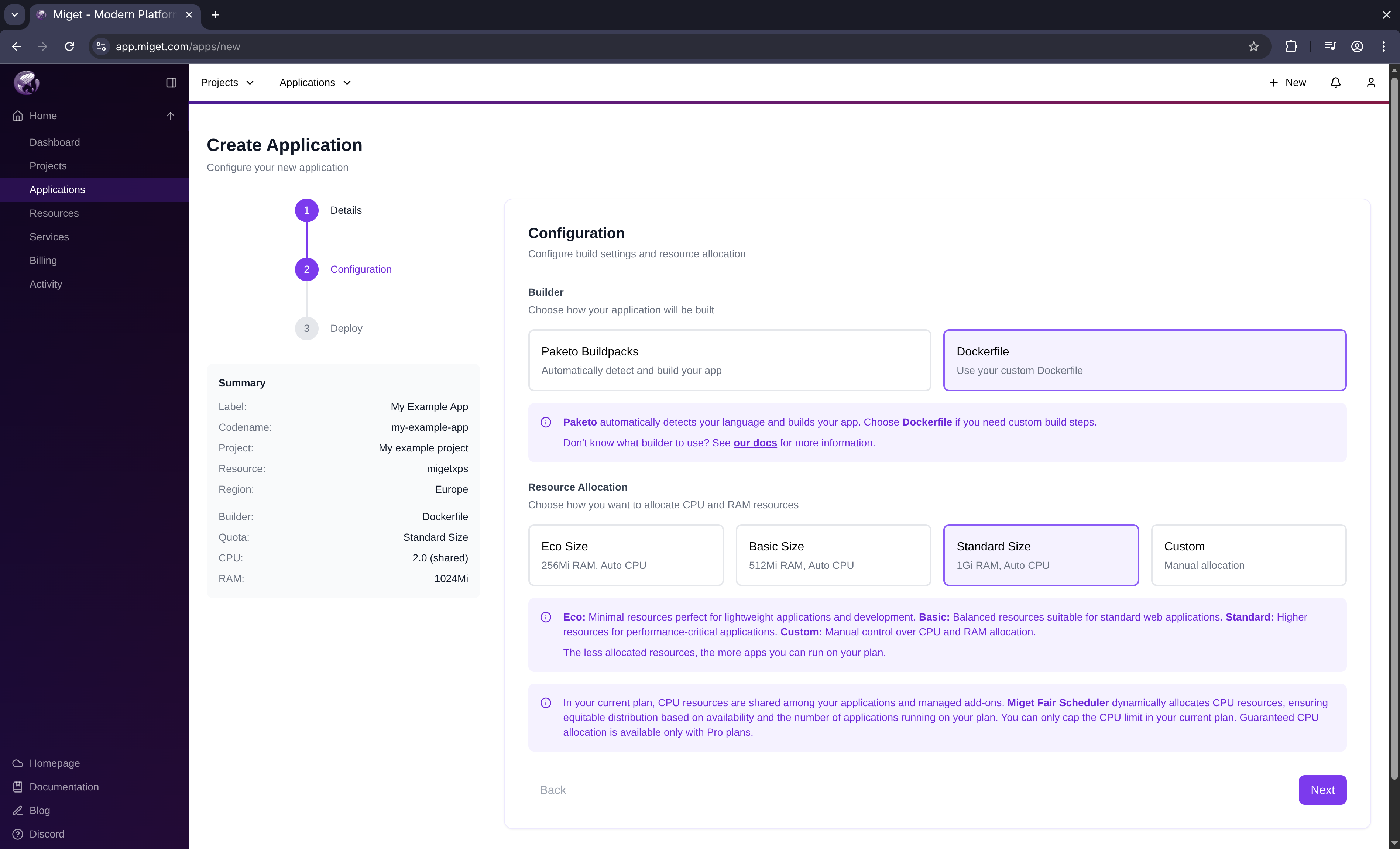
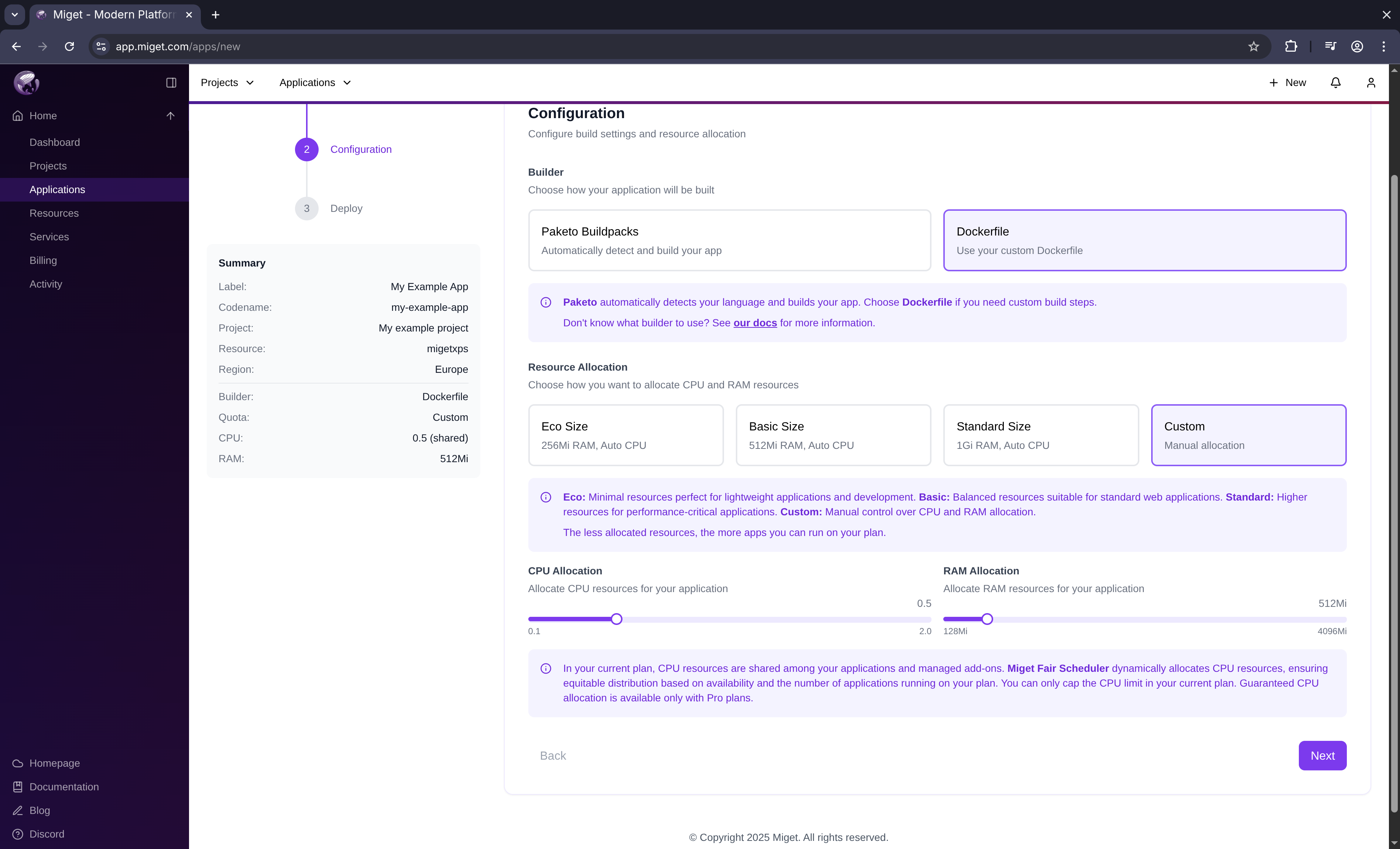

- Select Docker Engine as the builder type
- Choose a predefined size or specify custom resources
- Click Next

Select deploy method
Choose how you want to deploy your application: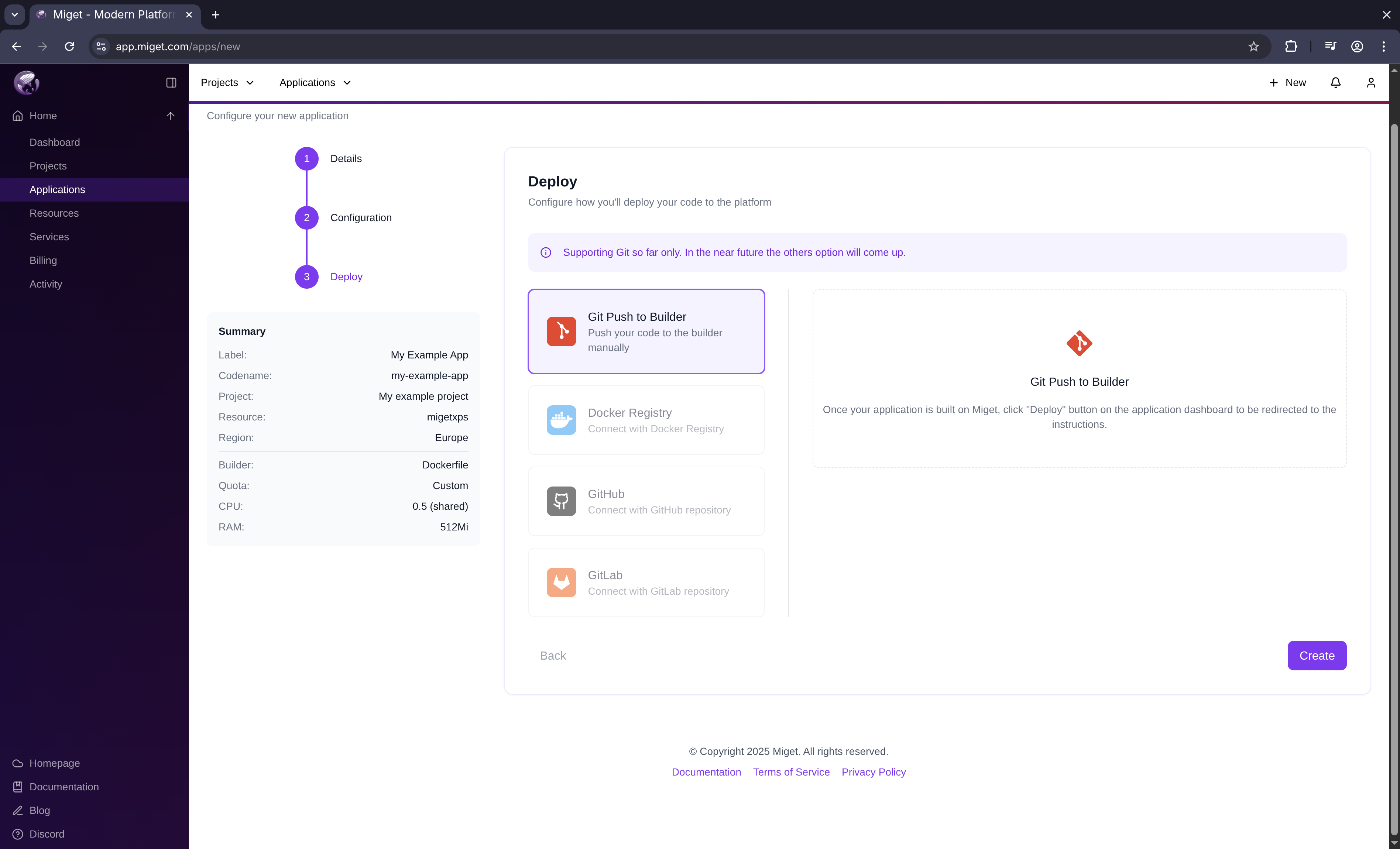

- Select git push as the deploy method
- Click Create
Currently,
git push is the only supported deploy method.You’re redirected to the app overview screen. Your app space (ingress, build context) is being created in the background.
Get your Git token
You need a Git token to push your code to Miget.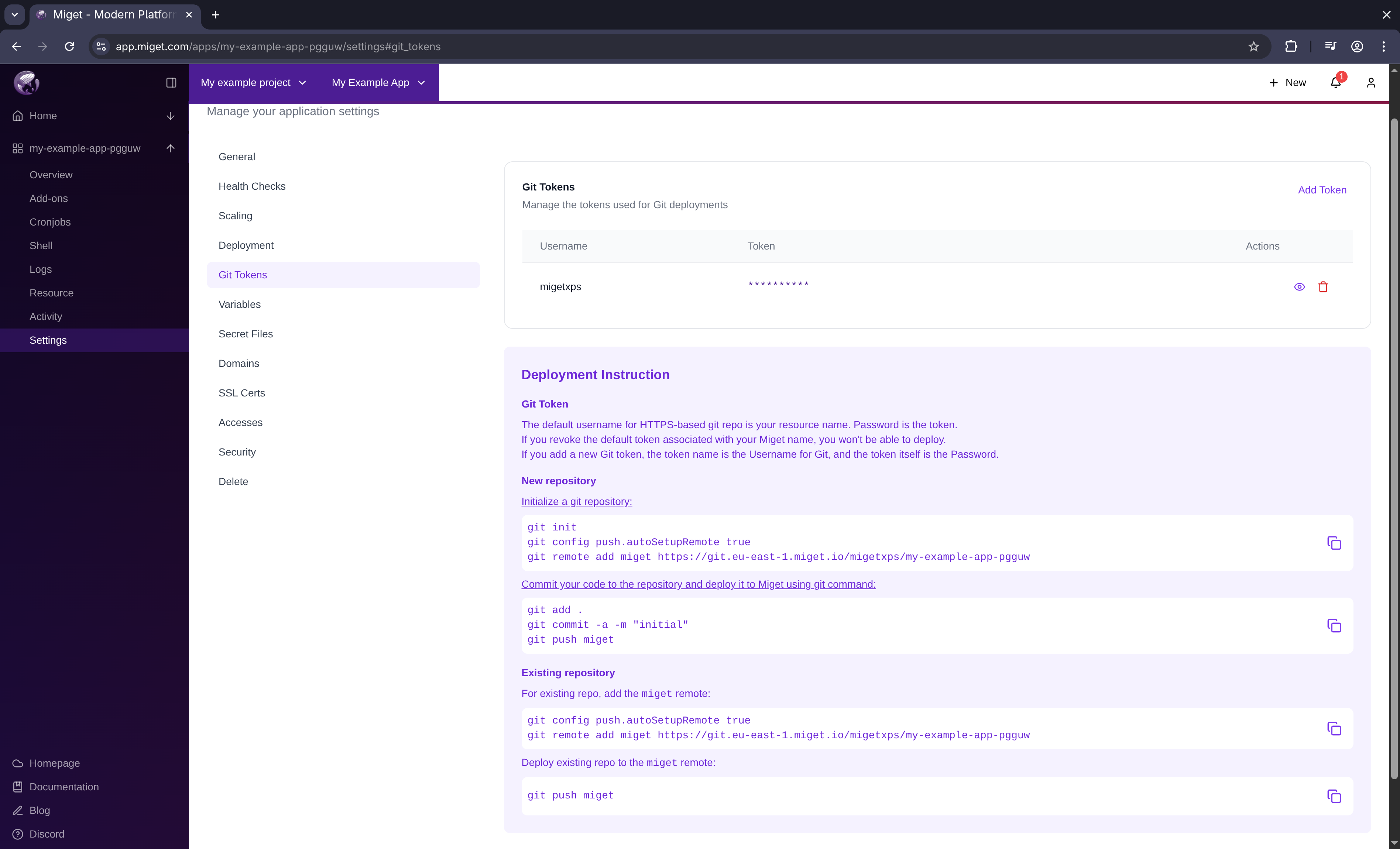

- Click the Deploy via git button
- Click See the token button
- Copy your token
- Your Miget name is the default username for Git
- The token is your password
- Revoking the default token prevents deployments
- Custom tokens use the token name as the username
Add Miget as a Git remote
Configure your local repository to push to Miget:Replace the placeholders:
<region>- Your Miget region code<your-miget-name>- Your compute resource name<app-name>- Your application name

