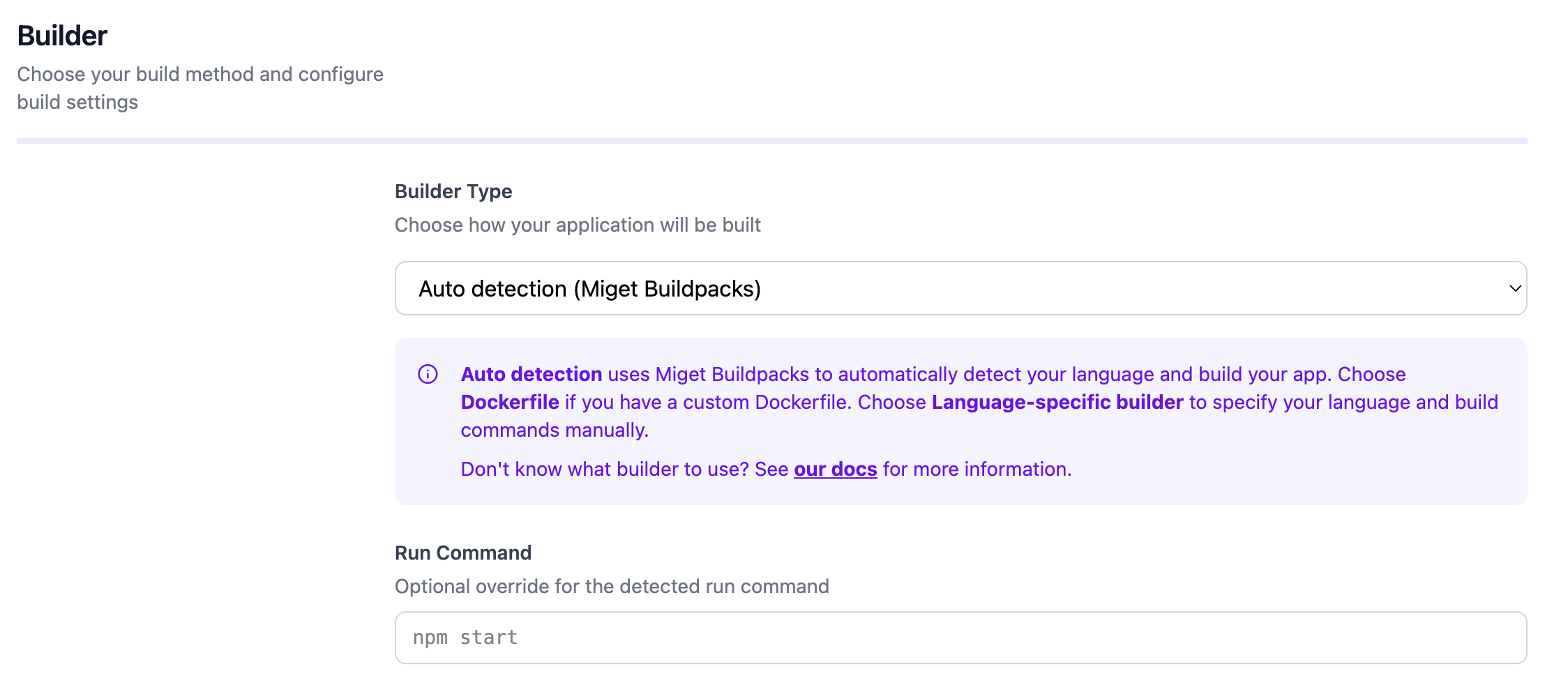
Detection
Your application is detected as Kotlin when both of these conditions are met:- A
build.gradle.ktsfile is present in the root directory .ktsource files exist in the project
Version Detection
The Kotlin version is determined from yourbuild.gradle.kts configuration. The Java version can be specified using a system.properties file at the root of your repository:
Build Process
During the build, the following steps are performed:- JDK installation - The appropriate version of the JDK is installed.
- Gradle build - Your application is built using Gradle. The Gradle Wrapper (
gradlew) is preferred if present; otherwise, a compatible version of Gradle is provided. - JAR packaging - The build produces a runnable JAR file.
Run Command
The run command is auto-detected from the JAR manifest’sMain-Class attribute.
You can override the run command by defining a web process in a Procfile at the root of your repository. You can also override the run command directly in the Miget dashboard when creating your app or changing the deployment source.
Configuration
You can customize the build and runtime behavior through the Miget dashboard and repository configuration files:- Environment variables - Set under Settings -> Variables in the Miget dashboard
- JAVA_OPTS - Pass JVM flags such as memory settings (e.g.,
-Xmx512m) - Procfile - Define the start command at the root of your repository
- Project Path - For monorepo setups, specify the subdirectory containing your application code in the Advanced tab
- Pre-Deploy Command - Run a command before deployment (e.g., database migrations) in the Advanced tab
- Post-Deploy Command - Run a command after successful deployment (e.g., seeding data, cache warming) in the Advanced tab
Docker Hardened Images
You can enable Docker Hardened Images (DHI) in the Advanced tab when creating your app or changing the deployment source. When enabled, your application is built using distroless runtime images with a minimal attack surface, no shell, and no package manager.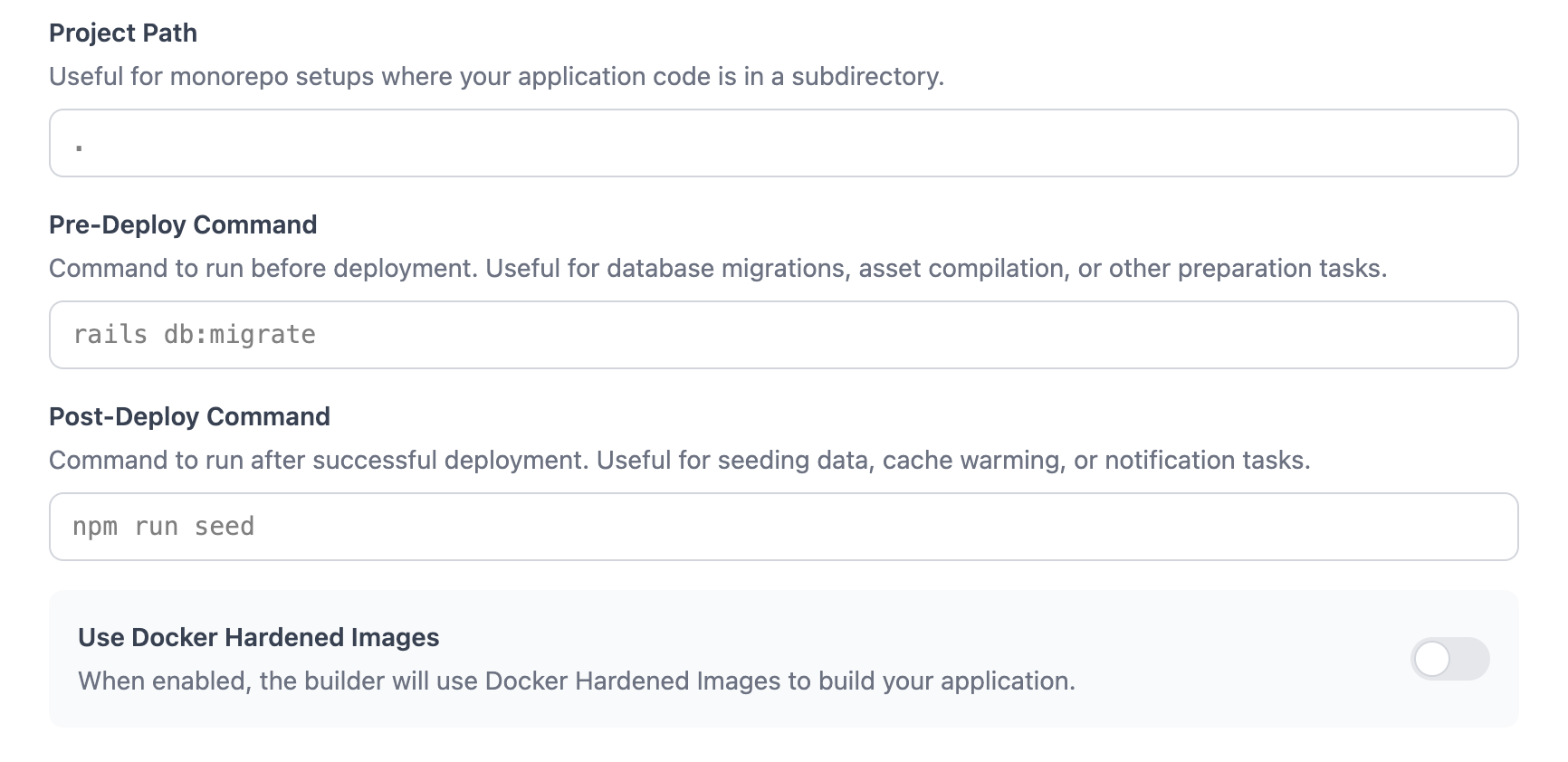
For the complete reference, see the migetpacks Kotlin documentation.

