Detection
Your application is detected as Ruby when one of these files is present in the root directory:GemfileRakefileconfig.ru
Version Detection
The Ruby version is determined from the following sources, in order of priority:.ruby-versionrubydirective inGemfile
Build Process
During the build, the following steps are performed:- Bundler version detection - The Bundler version is auto-detected from the
BUNDLED WITHsection inGemfile.lock. - Dependency installation - Gems are installed via Bundler.
- Native gem support - Native gems such as
pg,mysql2,sqlite3, andnokogiriare auto-detected, and the required system libraries are installed automatically. - Rails support - If Rails is detected:
- Asset precompilation runs automatically.
- Runtime cleanup removes unnecessary build artifacts.
Run Command
The run command is resolved in the following order:webprocess in aProcfile- Rails server (if Rails is detected)
rackup(ifconfig.ruis present)
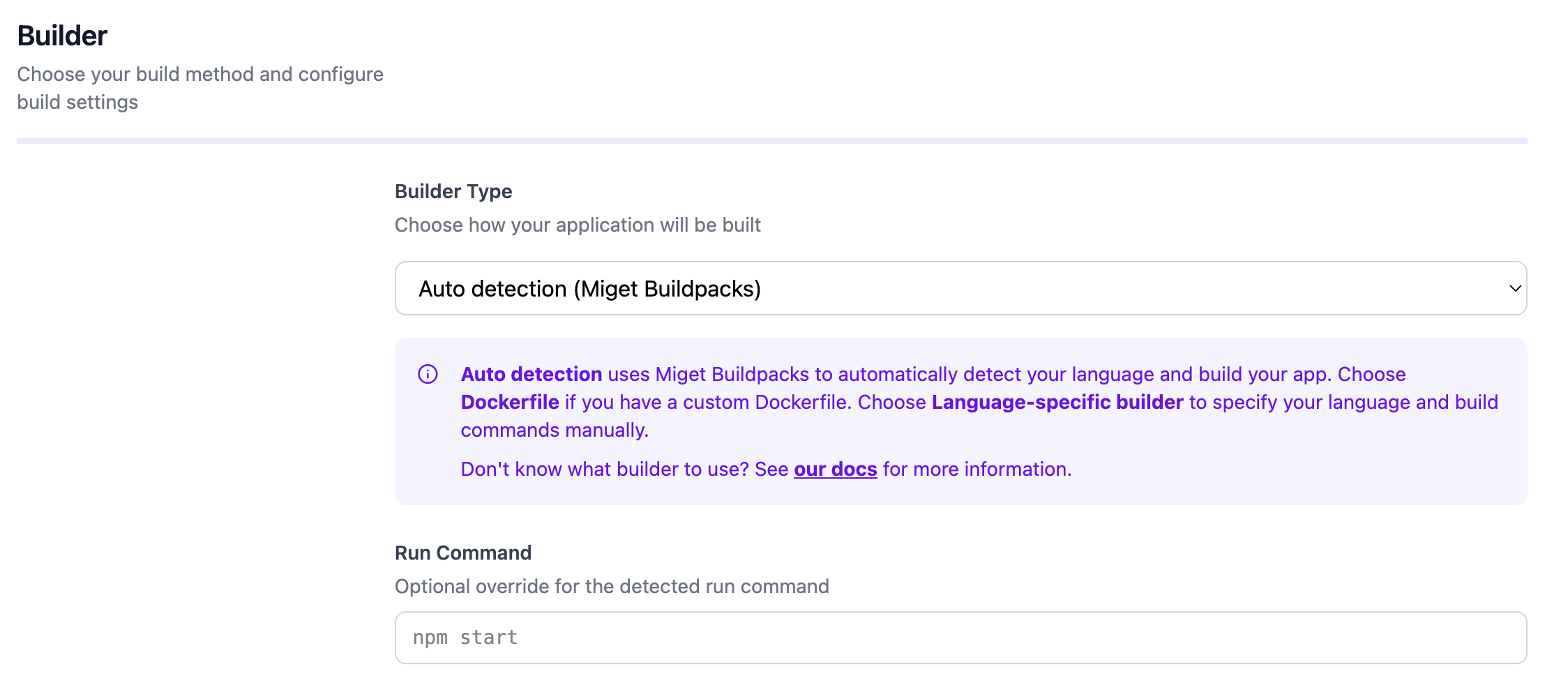
Configuration
You can customize the build and runtime behavior through the Miget dashboard and repository configuration files:- Environment variables - Set under Settings -> Variables in the Miget dashboard
- Procfile - Define the start command at the root of your repository
- app.json - Application manifest for additional configuration
- Project Path - For monorepo setups, specify the subdirectory containing your application code in the Advanced tab
- Pre-Deploy Command - Run a command before deployment (e.g., database migrations) in the Advanced tab
- Post-Deploy Command - Run a command after successful deployment (e.g., seeding data, cache warming) in the Advanced tab
Docker Hardened Images
You can enable Docker Hardened Images (DHI) in the Advanced tab when creating your app or changing the deployment source. When enabled, your application is built using distroless runtime images with a minimal attack surface, no shell, and no package manager.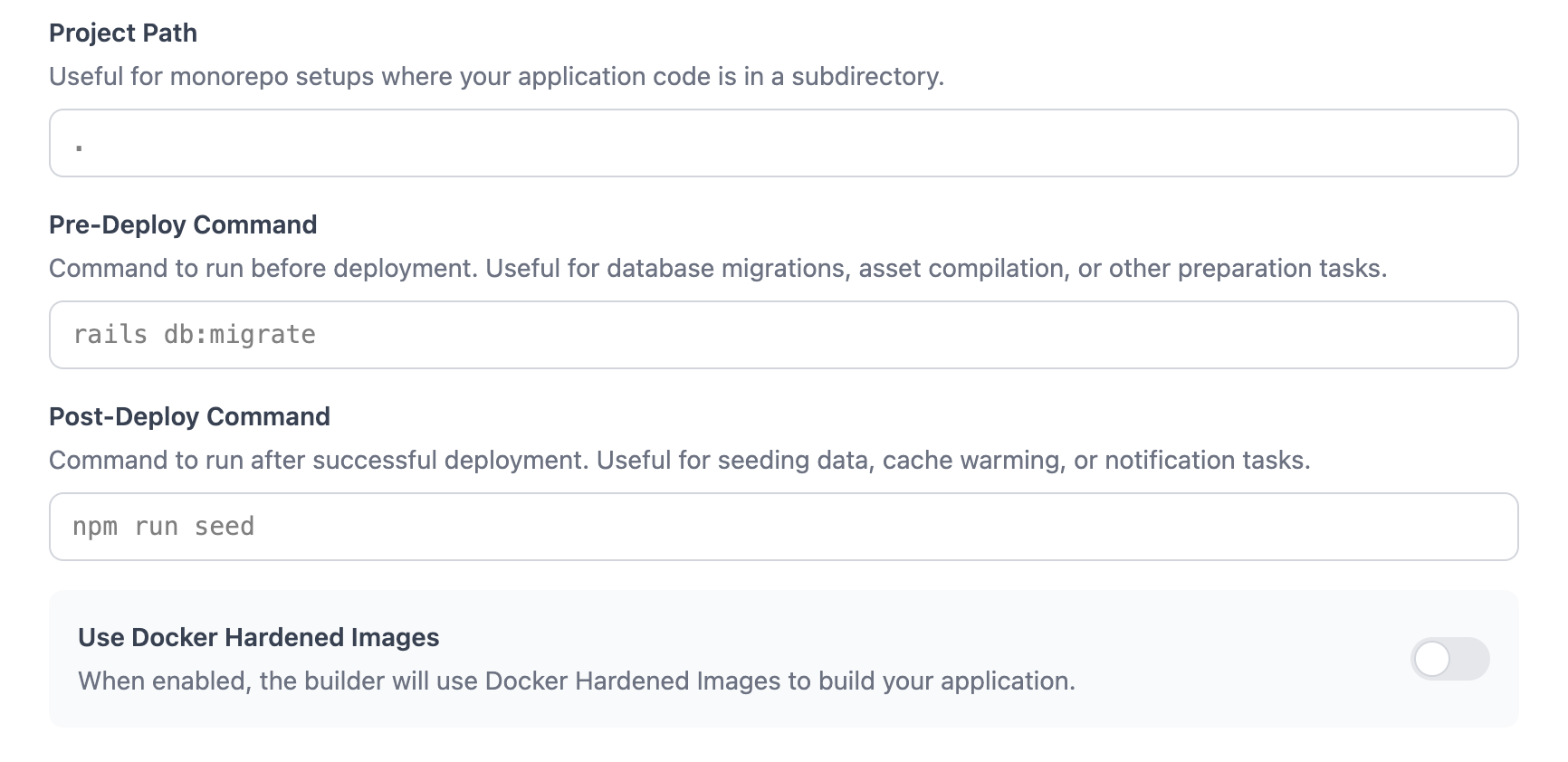
For the complete reference, see the migetpacks Ruby documentation.

